写在前面
比赛完蛋了,下次再来。
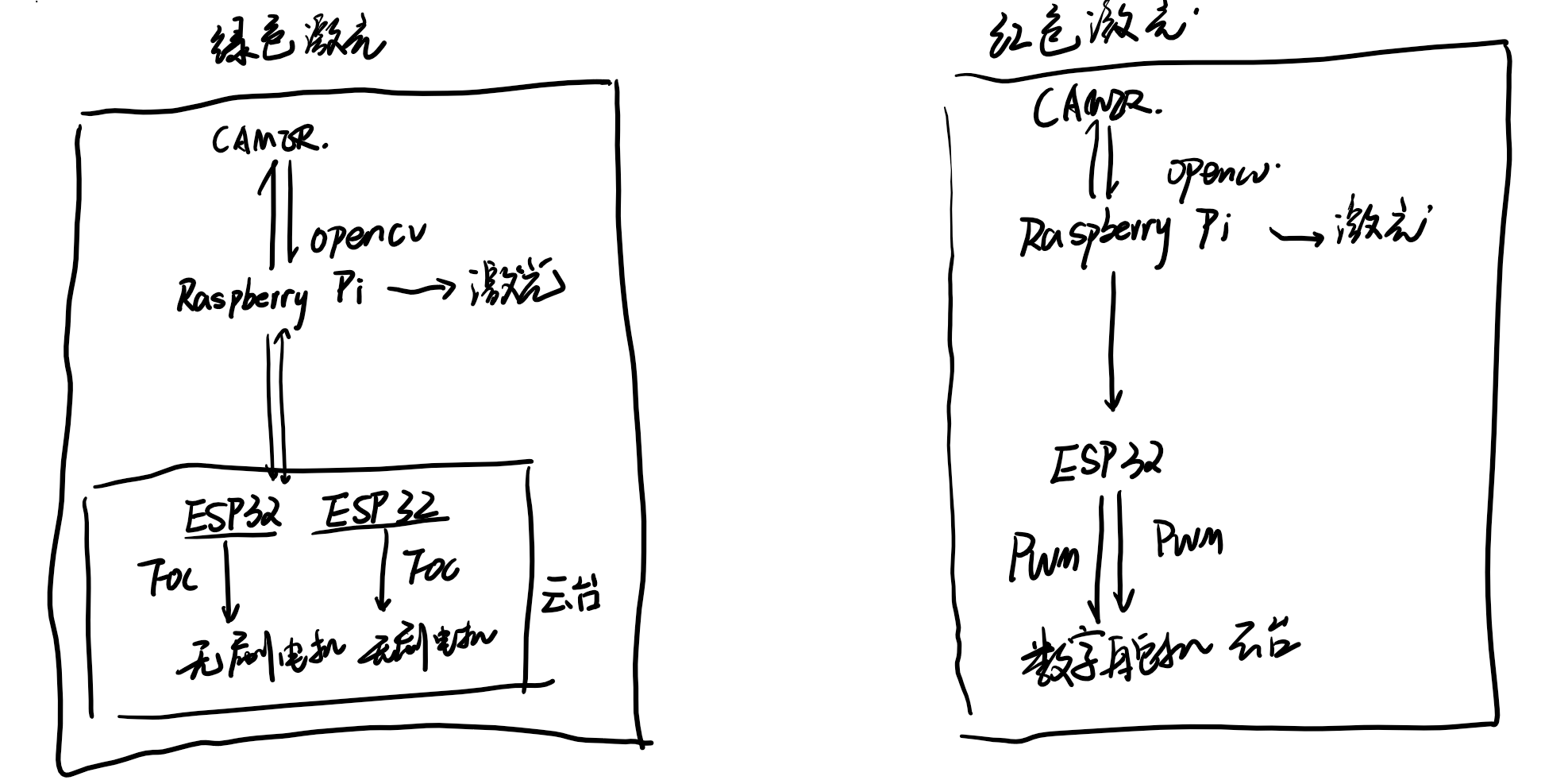
方案简介
硬件结构图
红色激光前两题题解
首先前两题我们的方案是直接使用开环控制。
直接记录舵机的pwm值,然后连续控制多级走四个点或者中心点即可。
红色激光第三题方案题解:
首先使用获取一张当前的图像,然后裁切得到一张只含有屏幕部分的该图像。
之后使用大津法进行选取,这样就能获取图片上面的黑框部分。
我们获取黑框的四个点之后可以对两个相邻点之间进行连续采样。
之后我们对舵机进行位置增量PID控制,来连续地追踪那一堆点。这样第三题就完成了。
绿色激光追踪题解
opencv首先hsv提取红色与绿色激光点位置,之后根据位置之差进行x,y方向的pid控制追踪,控制给到下位机的esp32,再控制无刷云台追踪实现闭环。
源码品鉴
无刷电机下位机程序
#include <SimpleFOC.h>
MagneticSensorI2C sensor = MagneticSensorI2C(AS5600_I2C);
BLDCMotor motor = BLDCMotor(11);
BLDCDriver3PWM driver = BLDCDriver3PWM(25, 26, 27, 14);
float target_angle = 0;
float change_angle = 2.8;
int i = 0;
Commander command = Commander(Serial);
void doTarget(char* cmd) { command.scalar(&target_angle, cmd); }
void setup() {
Wire.setPins(33,32);
Wire.begin();
sensor.init(&Wire);
motor.linkSensor(&sensor);
driver.voltage_power_supply = 12;
driver.init();
motor.linkDriver(&driver);
motor.foc_modulation = FOCModulationType::SpaceVectorPWM;
motor.controller = MotionControlType::angle;
motor.PID_velocity.P = 0.2f;
motor.PID_velocity.I = 20;
motor.PID_velocity.D = 0;
motor.voltage_limit = 6;
motor.LPF_velocity.Tf = 0.01f;
motor.P_angle.P = 20;
motor.velocity_limit = 10;
Serial.begin(115200);
motor.useMonitoring(Serial);
motor.init();
//motor.initFOC(4.58, Direction::CCW);
motor.initFOC(2.55, Direction::CW);
command.add('T', doTarget, "target angle");
_delay(1000);
}
void loop() {
motor.loopFOC();
//motor.move(target_angle - change_angle);
motor.move(change_angle - target_angle);
command.run();
i++;
if(i%5==0) {
Serial.println(sensor.getAngle());
i = 0;
}
}红色激光上位机程序
1. from class_driver.class_driver import motor_driver
2. import time
3. import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
4.
5. import cv2
6. import numpy as np
7.
8.
9. def get_points(img):
10. h = img.shape[0]
11. w = img.shape[1]
12.
13. for i in range(h): # 上
14. if 255 in img[i]:
15. white_index = np.where(img[i] == 255)
16. point_a = [i, white_index[0][0]]
17. break
18.
19. for i in range(w, 0, -1): # 右
20. if 255 in img[:, i - 1]:
21. white_index = np.where(img[:, i - 1] == 255)
22. point_b = [white_index[0][0], i]
23. break
24.
25. for i in range(h, 0, -1): # 下
26. if 255 in img[i - 1]:
27. white_index = np.where(img[i - 1] == 255)
28. point_c = [i, white_index[0][0]]
29. break
30.
31. for i in range(w): # 左
32. if 255 in img[:, i]:
33. white_index = np.where(img[:, i] == 255)
34. print('d:', )
35. point_d = [white_index[0][0], i]
36. break
37. return [point_a, point_b, point_c, point_d]
38.
39.
40.
41. last_x = 0
42. last_y = 0
43.
44. def img_get(img):
45. global last_x,last_y
46. size_min = 0
47. # 滤波二值化
48. # gs_frame = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (gs, gs), 1)
49. hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
50. # erode_hsv = cv2.erode(hsv, None, iterations=erode)
51. inRange_hsv = cv2.inRange(hsv, np.array([153, 98, 33]), np.array([179, 255, 255]))
52.
53. img = inRange_hsv
54. # 外接计算
55. cnts = cv2.findContours(img, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[-2]
56. target_list = []
57. if size_min < 1:
58. size_min = 1
59. for c in cnts:
60. if cv2.contourArea(c) < size_min:
61. continue
62. else:
63. target_list.append(c)
64. #print(target_list)
65. for cnt in target_list:
66. x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
67. # cv2.rectangle(img0, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
68. if len(target_list) == 0:
69. x = last_x
70. y = last_y
71. last_x = x
72. last_y = y
73. return x,y
74.
75. def round():
76. left_driver.raw = float(346)
77. left_driver.lll = float(382)
78. time.sleep(0.4)
79. left_driver.raw = float(303)
80. left_driver.lll = float(382)
81. time.sleep(0.4)
82. left_driver.raw = float(303)
83. left_driver.lll = float(325)
84. time.sleep(0.4)
85. left_driver.raw = float(346)
86. left_driver.lll = float(325)
87. time.sleep(0.4)
88.
89. def center():
90. # 回到中点
91. left_driver.raw = float(323) # 右小 左大
92. left_driver.lll = float(348) # 上大 下小
93.
94.
95. def mini_any(img):
96. point_human_1 = (200, 30)
97. point_human_2 = (460, 280)
98.
99. #point_human_1 = (0, 0)
100. #point_human_2 = (565, 460)
101. img = img[point_human_1[1]:point_human_2[1], point_human_1[0]:point_human_2[0]]
102. #print(img)
103. point_x,point_y = img_get(img)
104. return point_y,point_x
105.
106. def any(img):
107. left_driver.raw = float(333) # 右小 左大
108. left_driver.lll = float(339) # 上大 下小
109.
110.
111. #point_human_1 = (180, 30)
112. point_human_1 = (200, 30)
113. point_human_2 = (460, 280)
114.
115. #point_human_1 = (0, 0)
116. #point_human_2 = (565, 460)
117. img = img[point_human_1[1]:point_human_2[1], point_human_1[0]:point_human_2[0]]
118. #print(img)
119. point_x,point_y = img_get(img)
120. print(point_x,point_y)
121. img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
122.
123. retval, img = cv2.threshold(img,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
124.
125. #
126.
127. img = cv2.dilate(img, np.uint8(np.ones((3, 3))), 10)
128. img = cv2.bitwise_not(img)
129. ##img = cv2.erode(img, ,None, iterations=3)
130. cv2.imwrite("233.png",img)
131. box = get_points(img)
132. #print(img.shape)
133. print(box)
134. return box, point_x, point_y
135.
136.
137. def moive_point(mv_x,mv_y):
138. left_driver.raw = left_driver.raw-float(mv_x) # 右小 左大
139. left_driver.lll = left_driver.lll-float(mv_y)
140.
141. def list_cocu(x1,y1,x2,y2):
142. step = 20
143. fin_list = []
144. x_now = x1
145. y_now = y1
146. x_step = int(x2 - x1)/step
147. y_step = int(y2 - y1)/step
148. for i in range(0,step,1):
149. x_now = x_now + x_step
150. y_now = y_now + y_step
151. post = [x_now,y_now]
152. fin_list.append(post)
153. return fin_list
154.
155.
156.
157.
158. def control(list_list,delay):
159. kp = 0.01
160. kd = 0.001
161. ki = 0.02
162. kpa = 0.005
163. kda = 0.001
164. kia = 0.003
165. dt_y = 0
166. dt_x = 0
167. for ps in list_list:
168. print(ps)
169. for i in range(1,20):
170. all_error_x = 0
171. all_error_y = 0
172. error_past_x = 0
173. error_past_y = 0
174. ret, img = cap.read()
175. px,py = mini_any(img)
176. error_now_y = (ps[0] - px)
177. error_now_x = (ps[1] - py)
178. dt_y = error_now_y*kp - (-error_past_y +error_now_y)*kd + all_error_y *ki
179. dt_x = error_now_x*kpa - (-error_past_x +error_now_x)*kda + all_error_y *kia
180. error_past_x = error_now_x
181. error_past_y = error_now_y
182. all_error_x += error_now_x
183. all_error_y += error_now_y
184. print("px:"+str(px)+"py:"+str(py))
185.
186. moive_point(dt_x,dt_y)
187. #print(ps[0] - px,ps[1] - py)
188. #print(ps)
189. #print(px,py)
190. time.sleep(delay)
191.
192.
193.
194.
195.
196. if __name__ == '__main__':
197. cap = cv2.VideoCapture(-1)
198.
199. left_driver = motor_driver("/dev/left_roll",115200)
200.
201. left_driver.start()
202.
203. GPIO.setwarnings(False)
204. GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
205.
206. GPIO.setup(26,GPIO.IN,pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_DOWN)
207. GPIO.setup(27,GPIO.IN,pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_DOWN)
208. GPIO.setup(21,GPIO.OUT)
209. buzze = GPIO.PWM(21,1440)
210. buzze.start(0)
211.
212.
213.
214.
215.
216.
217.
218.
219. while True:
220. print(1)
221. if GPIO.input(27):
222. center()
223. print("center")
224. buzze.ChangeDutyCycle(50)
225. time.sleep(1)
226. buzze.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
227. elif GPIO.input(26):
228. round()
229. print("round")
230. buzze.ChangeDutyCycle(50)
231. time.sleep(1)
232. buzze.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
233. else:
234.
235. ret, img = cap.read()
236. kk,px,py=any(img)
237.
238. list_1 = list_cocu(kk[0][0],kk[0][1],kk[1][0],kk[1][1])
239.
240. list_2 = list_cocu(kk[1][0],kk[1][1],kk[2][0],kk[2][1])
241. list_3 = list_cocu(kk[2][0],kk[2][1],kk[3][0],kk[3][1])
242. list_4 = list_cocu(kk[3][0],kk[3][1],kk[0][0],kk[0][1])
243.
244.
245.
246. while not GPIO.input(26) or not GPIO.input(27):
247. control(list_1,0.02)
248. control(list_2,0.02)
249. control(list_3,0.02)
250. control(list_4,0.02)
绿色激光上位机程序
import cv2
from simple_pid import PID
from class_driver.class_driver import motor_driver
import time
import numpy as np
from simple_pid import PID
def getpoints(img, hsvmin, hsv_max, gs, erode):
img = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (gs, gs), 1)
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
hsv = cv2.erode(hsv, None, iterations=erode)
dst = cv2.inRange(hsv, hsvmin, hsv_max)
cnts = cv2.findContours(dst, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)[-2]
pos = []
for cnt in cnts:
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), 255, 2)
pos.append([int(x + w / 2), y + h / 2])
return pos
if __name__ == '__main__':
left_driver = motor_driver("/dev/left_roll",115200)
right_driver = motor_driver("/dev/right_roll",115200)
left_driver.start()
right_driver.start()
time.sleep(0.5)
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(-1)
pid_x = PID(0.0001, 0.0, 0.0, 0)
pid_y = PID(0.0001, 0.0, 0.0, 0)
try:
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
# red
red_points = getpoints(frame, np.array([144, 40, 138]), np.array([179, 255, 255]), 7, 0)
# green
green_points = getpoints(frame, np.array([46, 90, 179]), np.array([69, 206, 255]), 7, 0)
if len(red_points)==0:
print('NO red')
red_points = red
continue
else:
red = red_points.copy()
if len(green_points)==0:
print('NO green')
continue
else:
print(red_points[0], green_points[0])
error_x = green_points[0][0] - red_points[0][0]
error_y = green_points[0][1] - red_points[0][1]
move_y = pid_y(error_y)
move_x = pid_x(error_x)
if move_x>1:
move_x = 1
elif move_x<-1:
move_x = -1
if move_y>1:
move_y = 1
elif move_y<-1:
move_y = -1
left_driver.target_position = left_driver.target_position - move_y
right_driver.target_position = right_driver.target_position - move_x
print(error_x, error_y, left_driver.target_position, right_driver.target_position, move_x, move_y)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
left_driver.velocity = 0
right_driver.velocity = 0
time.sleep(0.1)
exit()上下位机通讯程序
import serial
import threading
import time
from simple_pid import PID
class motor_driver:
def __init__(self, port, baudrate):
self.motor_angle = 0
self.velocity = 0
self.target_position = 0
self.error = 0
self.serial_port = serial.Serial(
port=port,
baudrate=baudrate,
bytesize=serial.EIGHTBITS,
parity=serial.PARITY_NONE,
stopbits=serial.STOPBITS_ONE,
)
def start(self):
p = threading.Thread(target=self.serial_read, args=())
q = threading.Thread(target=self.serial_write, args=())
p.start()
q.start()
time.sleep(0.2)
def serial_read(self):
angle_str = ""
while 114514:
try:
if self.serial_port.inWaiting() > 0:
data = self.serial_port.read().decode()
if data == '\n':
self.motor_angle = float(angle_str)
angle_str = ""
else:
angle_str = angle_str + data
except:
self.velocity = 0
def serial_write(self):
while 114514:
data = 'T' + str(self.target_position) + '\n'
self.serial_port.write(data.encode())
time.sleep(0.02)
if __name__ == '__main__':
left_driver = motor_driver("/dev/left_roll",115200)
right_driver = motor_driver("/dev/right_roll",115200)
left_driver.start()
right_driver.start()
time.sleep(0.5)
try:
while True:
left_driver.motor_angle = 0
right_driver.motor_angle = 0
except:
left_driver.stop()
right_driver.stop()
print('stoped')
left_driver.velocity = 0
right_driver.velocity = 0
time.sleep(0.1)
exit()
现场测评为什么炸了
首先是第三题我们选择了HSV的图像筛选,但是到了比赛的地方我们发现实际的光线和实验室大相径庭,结果完全没有办法寻线,只得现场爆改摄像头亮度才能成功寻线,其次就是没有注意到第二组激光的摄像头要跟着云台走,结果导致了彻底的违规,所以很爆炸。
但是电赛还是我最喜欢的比赛
没有智能车那样强制限制主控类型,也没有那么各个队伍之间超级保密,大家真的是很友好,老师也很理解和提供帮助,总之就是下次还来。
